Introduzione ai pattern in C #
I motivi sono il disegno decorativo ripetuto. Esiste un semplice codice per scrivere modelli in C #. Possiamo scrivere codice per stampare diversi tipi di motivi come motivi a stelle, motivi a caratteri e motivi numerici. Di seguito sono riportati i vari esempi per stampare motivi di stelle, caratteri e valori numerici. Questi esempi sono costituiti da loop o loop nidificati che è un loop all'interno per un loop. I motivi sono un modo di progettare in sequenza o in modo logico. Possiamo stampare triangoli, piramidi, diamanti e altre simmetrie.
Primi 3 tipi di modelli in C #
I primi 3 tipi di modelli in c # sono menzionati di seguito.
1. Motivo a stella
I seguenti sono esempi per stampare motivi a stelle.
Esempio 1
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y, z;
for (x =6; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 1; y < x; y++)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (z = 6; z >= x; z--)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:

Esempio n. 2
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 6; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:

Esempio n. 3
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:

Esempio n. 4
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y, z;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 5; y > x; y--)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (z = 1; z <=x; z++)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:

Esempio n. 5
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y, z;
for (x= 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = x; y < 5; y++)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (z = 1; z < (x * 2); z++)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:

Esempio n. 6
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y, z;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 5; y > x; y--)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (z = 1; z < (x * 2); z++)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:

Esempio n. 7
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = x; y < 5; y++)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (y = 1; y <= (2 * x - 1); y++)
(
if (x == 5 || y == 1 || y == (2 * x - 1))
(
Console.Write("*");
)
else
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:

Esempio n. 8
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= 5; y++)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:

Esempio n. 9
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
if (y == 1 || y== x || x == 5)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
else
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:

2. Schemi numerici
Di seguito sono riportati esempi per stampare modelli numerici.
Esempio 1
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
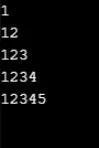
Esempio n. 2
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
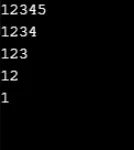
Esempio n. 3
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = x; y <= 5; y++)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
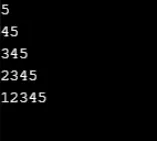
Esempio n. 4
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = x; y <= 5; y++)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
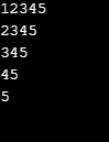
Esempio n. 5
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write(x);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
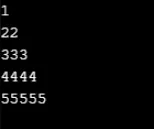
Esempio n. 6
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 5; y >= x; y--)
(
Console.Write(x);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
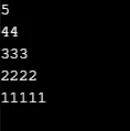
Esempio n. 7
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write(x);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
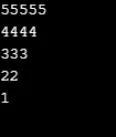
Esempio n. 8
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = 5; y >= x; y--)
(
Console.Write(x);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
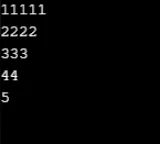
Esempio n. 9
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 6; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = x; y >= 1; y--)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
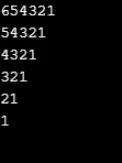
Esempio n. 10
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = 6; y >= x; y--)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
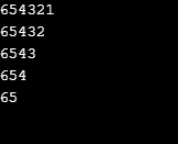
Esempio n. 11
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 7; x >= 1; x -= 2)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
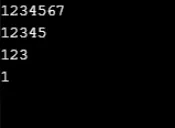
3. Motivo del personaggio
Il Di seguito sono riportati esempi per stampare motivi di caratteri.
Esempio 1
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int z = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= z; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write((char)(x + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
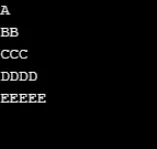
Esempio n. 2
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int z = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= z; x++)
(
for (y = x; y <= z; y++)
(
Console.Write((char)(x + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
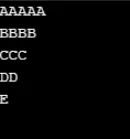
Esempio n. 3
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int z = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= z; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write((char)(z - x + 1 + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
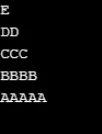
Esempio n. 4
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int z = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= z; x++)
(
for (y = x; y<= z; y++)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
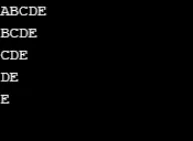
Esempio n. 5
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y, z;
int k = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= k; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= k - x; y++)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (z = 1; z <= x; z++)
(
Console.Write((char)(x + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:

Esempio n. 6
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int a = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= a; x++)
(
for (y = x; y >= 1; y--)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
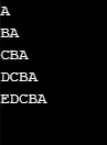
Esempio n. 7
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int a = 5;
for (x = a; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = a; y >= x; y--)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
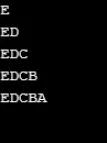
Esempio n. 8
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int a = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= a; x++)
(
for (y = a; y >= x; y--)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
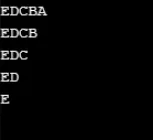
Esempio n. 9
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int z = 5;
for (x = z; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = x; y >= 1; y--)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:
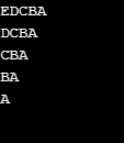
Esempio n. 10
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int z = 6;
for (x = 1; x <= z; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y<= z - x; y++)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
for (y = x - 1; y >= 1; y--)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Produzione:

Conclusione
Così sopra sono riportati alcuni esempi di vari tipi di modelli. Siamo in grado di stampare qualsiasi tipo di motivo con alcune modifiche nei cicli.
Articoli consigliati
Questa è una guida ai Pattern in C #. Qui discutiamo l'introduzione e i primi 3 tipi di Pattern in C # insieme ai suoi esempi e all'implementazione del codice. Puoi anche consultare i seguenti articoli per saperne di più-
- Cos'è Design Pattern in C #?
- Domande di intervista sul modello di progettazione C #
- Matrici 2D in C #
- Sostituzione in C #
- Sostituzione in Java
- 3 diversi tipi di array in PHP (esempi)
- Pattern numerici in Java con esempi